​what Is Abnormal Backflow of Urine From the Bladder to the Ureter Called?
Hither we are providing Class eleven Biological science Important Actress Questions and Answers Affiliate 19 Excretory Products and their Emptying. Important Questions for Class 11 Biology are the best resource for students which helps in Class 11 board exams.
Class 11 Biology Affiliate xix Important Extra Questions Excretory Products and their Emptying
Excretory Products and their Elimination Important Actress Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is a nephron?
Answer:
The functional unit of the kidney.
Question 2.
What is a flame prison cell?
Answer:
The excretory unit in planaria, tapeworm, and liver fluke.
Question 3.
What is micturition?
Answer:
It is the human action of void of the urinary bladder, the activity nether nervous and voluntary command.
Question iv.
What are ammonotelic animals?
Reply:
The animals which excrete nitrogenous wastes equally ammonia are ed ammonotelic animals, e.k., certain fishes.
Question 5.
What is a green gland and in which animal it is found?
Answer:
It is an excretory structure institute in prawns.
Question 6.
What is an antidiuretic hormone?
Reply:
It is the hormone that helps in the reabsorption of h2o in the nephron, as well called vasopressin (Secreted past mail service pituitary gland).
Question 7.
Ascertain excretion.
Answer:
Excretion is the process of emptying of metabolic wastes from the torso.
Question 8.
What is the color rendering substance found in urine?
Answer:
Urochrome.
Question 9.
What are diuretics?
Answer:
The substances which increase the book of water, to be excreted as urine, are called diuretics, e.g., tea, coffee, alcoholic beverages.
Question 10.
What is osmoregulation?
Reply:
Information technology is the maintenance of h2o and osmotic concentration of blood.
Question 11.
Name the organ of the excretory system, which stores urine before its removal from the torso.
Answer:
Urinary bladder.
Question 12.
In which part of the nephron does filtration occur?
Answer:
Glomerulus.
Question thirteen.
What happens to the useful substances that get filtered into the renal tubule?
Answer:
They are reabsorbed into the blood.
Question 14.
Point out the master excretory organ?
Answer:
Kidney.
Question fifteen.
Write down the products excreted by the following organs.
(a) Lung
Reply:
Lung: Carbon dioxide and water vapor
(b) Skin,
Answer:
Skin: Urea, water, and some salts
(c) Intestine.
Answer:
Intestine: Some salts similar calcium and iron.
Question 16.
What is excreted by the kidney in urine?
Answer:
Urea.
Question 17.
In which part of the nephron does filtration occur?
Answer:
Glomemle.
Question eighteen.
Who filters the blood?
Answer:
The kidney filters the claret, which takes place between the glomerulus and Bowman'southward capsule.
Question 19.
Why it is necessary to remove waste products past excretion?
Reply:
It is essential and necessary because all waste products are toxic and harmful.
Excretory Products and their Emptying Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question i.
Differentiate between sweat and sebum.
Answer:
| Sweat | Sebum |
| 1. It is a liquid state excretion of can. | ane. Information technology is semisolid excretion |
| 2. NaCl. urea, amino-acids are excreted. | ii. Waxes, fatty acids, and sterol are excreted. |
| 3. Excreted in large amounts | three. Excreted in small-scale amounts |
| iv. Too thermoregulatory role. | 4. No thermoregulatory role. |
Question 2.
What consequences will follow with the failure of tubular reab¬sorption in nephrons?
Reply:
Nephrons are the structural and functional units of each kidney. With the failure of reabsorption in nephrons, much-needed substances like glucose, amino acids, h2o, salts, etc. will be excreted along with urine.
The biological functioning of organs and torso will be impaired, ultimately death will occur.
Question 3.
How the net filtration pressure is obtained?
Answer:
The force per unit area of blood in afferent arterioles is (+ mm Hg 75). This is opposed past the osmotic pressure of plasma proteins past (-) 30 mm Hg and intertubular pressure level of (-) 20 mm Hg. The cyberspace filtration pressure is (+) 25 mm Hg that acts in glomerular filtration as a driving strength. About 172 liters of glomerular filtrate are produced in 24 hrs. which is virtually iv-1/ 2 times the total fluid in the human body.
Question 4.
Listing some important functions of kidneys?
Reply:
Kidneys play a vital role as follows:
(a) Information technology removes nitrogenous wastes from the blood.
(b) It regulates fluid residual, betwixt intake and fluid loss.
(c) It removes drugs, penicillin, poisons, etc. from blood.
(d) Information technology maintains acid-base (pH) residual
(east) Information technology regulates electrolyte balance.
Question v.
Differentiate between ureter and urethra?
Respond:
| Ureter | Urethra |
| 1. It is a muscular tube. | 1. It is a membranous tube. |
| 2. It is long. | 2. It is brusk. |
| 3. It arises from the renal pelvis of the kidney. | iii. It arises from the urinary bladder. |
| 4. Information technology carries urine to the urinary bladder. | 4. It eliminates stored urine of the exterior. |
| 5. No muscular splincter. | 5. Muscular splinter keeps urethra-closed except for micturition. |
Question half dozen.
How does the excretion of uric acid accept place in birds and reptiles?
Answer:
In birds and reptiles, uric acid is formed mostly in the liver, transported to the kidney through blood. It is separated past renal tubules and temporarily stored in cloacae. Water is captivated by cloacal walls, needing only a minimum amount of h2o for excretion. In birds, urine is eliminated in a paste-like form along with feces.
Question 7.
Name and state in brief the processes involved in the formation of urine.
Answer:
The urine is formed by the combined processes every bit follows:
(a) Glomerular filtration: Metabolism wastes and other substances are filtered out by glomerulus due to the generation of net filtration force per unit area.
(b) Re-absorption: Water and other required substances are selectively reabsorbed from the filtrate, then that urine becomes concentrated.
(c) Tubular secretion: Tubules secrete certain ions (like K+ in exchange for Na+), urea, creatinine, uric acid, ammonia, etc. This process is of more significance in marine fishes and desert amphibians than mammals.
Question 8.
Differentiate between ureotelism and Uricotelism.
Reply:
| Ureotelism | Uricotelism |
| 1. The process of emptying of main urea. | one. The process of elimination of mainly uric acid. |
| 2. Water moderately required for excretion. | 2. Much less water required for excretion. |
| 3. Synthesis of urea requires less energy expenditure. | 3. Synthesis of uric acrid needs more energy expenditure. |
Question ix.
What is Polynephritis? What is uremia?
Answer:
It is a bacterial infection that causes inflammation of the renal pelvis, nephrons, and medullary tissues of the kidney. It affects the counter-electric current mechanism. Its main symptoms are frequent and painful urination, fever, and pain in the lumbar region.
A high concentration of urea, uric acid, creatinine, etc. in the blood due to some bacteria infection or some obstruction in the passage of the urinary arrangement is called uremia.
Question ten.
Point whether the following statements are True or False
(a) Micturition is carried out by a reflex.
Answer:
True
(b) ADH helps in h2o elimination, making the urine hypotonic.
Reply:
False
(c) Protein-complimentary fluid is filtered from claret plasma into the Bowman'due south capsule
Answer:
True
(d) Henle'due south loop plays an of import role in concentrating the urine.
Answer:
Truthful
(e) Glucose is actively reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule.
Respond:
True
Question 11.
Match the items of Cavalcade I with these of Cavalcade Ii.
| Column I | Column-2 |
| (a) Ammonotelism | (i) Birds |
| (b) Bowman'south Capsule | (ii) Hypertonic urine |
| (c) Micturition | (iii) Counter-electric current system |
| (d) Uricotelism | (iv) Bony fish |
| (e) Vasa recta | (five) Urinary bladder |
| (f) Sebum | (vi) Glucose |
| (g) ADH | (vii) Glomerular Alteration |
| (h) Tubular reabsorption | (viii) Skin |
Answer:
| Column I | Column-II |
| (a) Ammonotelism | (iv) Bony fish |
| (b) Bowman'due south Capsule | (vii) Glomerular Amending |
| (c) Micturition | (five) Urinary float |
| (d) Uricotelism | (i) Birds |
| (e) Vasa recta | (three) Counter-current organisation |
| (f) Sebum | (viii) Skin |
| (m) ADH | (ii) Hypertonic urine |
| (h) Tubular reabsorption | (6) Glucose |
Question 12
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
(a) During micturition, the urinary bladder, and the urethral sphincters contract, and relax
(b) Flame cells and malpighian tubules are found in and Bowman's capsule and glomerulus respectively.
(c) Blood enters the glomerulus through the renal arteriole and leaves via the afferent arteriole.
(d) Ii counter-current systems formed in the kidney are the Renal medulla and the renal cortex
(e) Sweat serves to eliminate mainly h2o and table salt
Question 13.
Compare and dissimilarity the osmoregulatory issues and adaptations of a marine bony fish with a freshwater bony fish.
Answer:
Osmoregulation in freshwater Marine bony fish, do non drink water to reduce the demand to expel excess water. In this case, water uptake and salt loss are minimized by a specialized trunk covering. Freshwater animals take the ability to have upwards salts from the environment. The active transport of ions takes place against the concentration slope, specialized cells called monocytes or chloride cells in the gill membrane of freshwater fish. These can import Na+ and CI– from the surrounding water containing less than i mm NaCl when their plasma concentration of NaCl exceeds 100 mm.
Osmoregulation in marine surroundings Seawater has an osmolarity of almost 1000m Osm L The osmoregulatory problems in marine water are contrary to those in a freshwater surround. Marine bony fish have the body fluids hypotonic to seawater and thereby, they tend to lose h2o from the body through permeable surfaces.
To compensate for the water loss, marine bony fish drink seawater, which results in a gain of excess salts. The monocytes or chloride cells of the gill membrane of marine bony fish help to eliminate excess monovalent ions from the body fluid to the seawater. Divalent cations are generally eliminated with feces.
Question 14.
Land the importance of counter-current systems in renal functioning.
Answer:
Vasa rectal is responsible for the concentration of urine. The vase rectal is in the form of loops. Therefore, the blood flows in the reverse directions in 2 limbs of each vasa Fecta; the claret inbound its descending limb comes into close contact with the outgoing blood in the ascending limb. This is called a Counter-Electric current System. The two limbs of the loops of Henle class another Counter-Current System.
Importance: The counter-current system significantly contributes to concentrating urine in mammals.
Question 15.
State the position and function of the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
Respond:
This is a specialized cellular appliance located where the distal convoluted tubule passes close to the Bowman's sheathing between the afferent and efferent arterioles. JGA cells secrete substance like renin that modulates claret pressure and renal blood catamenia and thus, GFR is regulated.
Question 16.
Depict the hormonal feedback circuits in controlling renal functions.
Answer:
Two important hormonal control of the kidney office by negative feedback circuits can be identified:
ane. Command past Antidiuretic Hormone ADH: ADH produced in the hypothalamus of the brain and released into the blood from the pituitary gland, enhances fluid retentivity by making the kidneys reabsorb more water. The release of ADH is triggered when osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus detect an increase in the osmolarity of the blood.
The osmoreceptors cells also promote thirst. Drinking reduces the osmolarity of the claret which inhibits the secretion of ADB, thereby completing the feedback circuit.
2. Command by Juxtaglomerular Appliance (JGH): Information technology operates a multihormonal Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS). JGA responds to subtract the blood force per unit area and release enzyme renin into the blood. In the blood, the enzyme initiates chemical reactions that convert a plasma protein chosen angiotensinogen to a peptide called angiotensin II which works as a hormone.
Angiotensin Ii increases blood pressure and stimulates the adrenal gland to release aldosterone, a hormone. This leads to an increase in blood book and pressure level completing the feed¬back circuit past supporting the release of renin.
Still another hormone, a peptide called Atrial Natriuretic Gene ANF), opposes the regulation by RAAS.
Thus, ADH, the RAAS, and ANF provide an elaborate system of checks and balance that regulate the kidney functioning to control body fluid, osmolarity, table salt concentration, blood pressure level, and claret volume.
Question 17.
State the normal and abnormal constituents of human being urine.
Answer:
Urine is a pale yellow colored slightly acidic watery fluid.
- Aberrant Urine: Diverse metabolic errors of kidney malfunctioning changes the composition of urine.
- Proteinuria: Backlog of protein level.
- Albuminuria: The presence of albumin, usually occurs in nephritis.
- Glycosuria: Presence of glucose in urea as in instance of diabetes mellitus.
- Ketonuria: Presence of abnormally high ketone bodies.
- Hematuria: Presence of blood or blood cells in urine.
- hemoglobinuria: Presence of hemoglobin in urine.
- Uremia: Presence of excess urea.
- Normal Urine: Normal urine is slightly heavier than water. It gives an effluvious odor due to the presence of volatile, bad-smelling organic substances, the ruined water, organic and inorganic materials are the main constituents of normal urine.
The other nitrogenous constituents of normal urine are ammonia, uric acid, hippuric acid, and creatinine.
Non-nitrogenous substances are vitamin C, oxalic acid, phenolic substances. In inorganic substances, sodium chloride is the principal mineral salt in the urine.
Question xviii.
State the role of skin and lungs in excretion.
Answer:
Role of Peel: Man skin possesses glands for secreting sweat and sebum (from the sebaceous gland). Sweat contains NaCl, lactic acrid, urea, amino acids, and glucose. The volume of sweat various negligible to 14 Fifty a day. The principal role of sweat is the evaporative cooling of the torso surface.
Sebum is a waxy protective secretion to proceed the skin oily and this secretion eliminates some lipids, such every bit waxes, sterols, other hydrocarbons, and fatty acids. Integument in many animals is excreting ammonia into the surrounding by improvidence.
Role of lungs in excretion: Human lungs eliminate around 18L of COtwo per day and about 400 ml of water in normal resting conditions. Water loss via lungs is pocket-sized in hot humid climates and large in cold dry climates. The rate of ventilation and ventilation design as well affects the water loss through the lungs. Different volatile materials are besides readily eliminated through the lungs.
Excretory Products and their Emptying Important Extra Questions Long Reply Blazon
Question 1.
Briefly land the mechanism of urine formation in the human kidney.
Respond:
Three main processes are involved in urine germination
i. Glomerular filtration: Kidneys filter the equivalent of blood book every 4 – 5 minutes. Filtration slits are formed by the assemblages of fine cellular processes of podocytes (foot cells). The process of ultra-filtration depends upon ii main factors, first the net hydrostatic pressure deviation between the lumen of the capillary and the lumen of the Bowman's capsule favor filtration.
The glomerular ultrafiltrate contains substantially all the constituents of the claret except for blood corpuscles and plasma proteins. About 15% – 25% of the water and salutes are removed from the plasma that flows through the glomerulus. The glomerular filtration rate is about 125 ml min1 or about 180 Fifty mean solar day-one in human kidneys.
2. Two of import intrinsic mechanisms provide autoregulation of glomerular filtration charge per unit.
(a) Myogenic mechanism: Increase in blood force per unit area will tend to stretch the efferent arteriole, which would increase the blood period to the glomerulus. The diameter of the arteriole is reduced, increasing the resistance to flow. This myogenic mechanism thus reduced variations inflow to the glomerulus in case of fluctuations in claret force per unit area.
(b) Juxtaglomerular appliance (JGA): This specialized cellular appliance is located where the distal convoluted tubule passes close to the Bowman's capsule betwixt the afferent and efferent arterioles. JGA cells secrete substances similar renin that modulate blood force per unit area and renal blood catamenia and GFR are regulated.
Myogenic and juxtaglomerular mechanisms work together to autoregulate the GFR over a wide range of blood pressure. In improver to these extrinsic neural control also regulates the filtration rate.
3. Tubular re-absorption: The selective transport of substances beyond the epithelium of the excretory tubule from the ultrafiltrate to the interstitial fluid is called re-absorption. Almost all the sugar, vitamins, organic substances (nutrients), and almost of the water are reabsorbed.
four. Tubular secretion: It is a very selective process involving both passive and active transport. The filtrate travel through the nephron, substances that are transported beyond the epithelium from the surrounding interstitial fluid and join it. The net event of renal secretion is the addition of plasma solutes to the filtrate within the tubule.
Question 2.
Explain the following:
(a) Skin functions as an accompaniment excretory organ.
Answer:
The pare retains some excretory function in many animals. Human peel possesses two glands for secreting fluid on its surface. These are; sweat from sweat glands and sebum from sebaceous glands.
(b) Mammals tin can eliminate hypotonic and hypertonic urine co-ordinate to body needs.
Reply:
When the fauna takes a big quantity of h2o the kidneys excrete a very high amount of hypotonic urine. At the same fourth dimension when the animal takes a pocket-size number of water kidneys to excrete a very high amount of hypertonic urine.
At the same fourth dimension when the animal takes a pocket-size number of water kidneys to excrete a small amount of hypertonic urine, equally kidneys demand to conserve water. In this way, the osmotic concentration of blood is maintained by the kidneys. This flexibility of kidney nephrons is highly observed in mammals.
Hypotonic urine removes backlog water from the body in order to raise the osmotic concentration of the blood to normal. Excess of h2o in body fluids generally lowers the osmotic force per unit area of blood and increases the book of blood. This increment in the volume of blood raises the blood pressure and hydrostatic pressure which increases the rate of ultrafiltration. In this fashion, a big amount of hypotonic urine is produced in society to bring the volume of fluids to normal.
(c) Micturition is a reflex process merely is under some voluntary control.
Answer:
Information technology is the process of passing out urine. Nephrons produce urine and drain. When enough urine collects in the bladder the amplification of its walls raises enough force per unit area which generates a spontaneous nervous activity under the stimulation of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. This nervous stimulation causes the shine muscles on the urinary float to rise too high to control.
Similarly, micturition tin voluntarily be initiated even before plenty urine has accumulated in the bladder. Backflow of the urine into the ureters from the urinary float is prevented because the terminal office of each ureter passes through the bladder and gets closed every bit soon as the wrinkle of the float occurs.
(d) Mammals are ureotelic, but birds are uricotelic.
Reply:
Mammals are ureotelic animals every bit they eliminate nitrogen mainly urea. It is very soluble in h2o and needs a considerable amount of water for its elimination. Mammals can thus class hypertonic urine which they excrete. While the birds cannot excrete urine as hypertonic since nitrogen occurs mainly in the form of uric acid. The uric acrid is insoluble in h2o and does not require much water for its elimination.
Question three.
Describe the functional anatomy of a human nephron.
Reply:
Nephrons are structural and functional units of each kidney to form the urine. Each nephron is fine; microscopic highly coiled tubular construction differentiated into malpighian torso and the renal tubule. The malpighian body comprises a large double-walled loving cup-shaped structure the Bowman'southward capsule present in the renal cortex. Information technology is lined by thin, semipermeable epithelial cells, the podocytes. Bowman's capsule receives the claret supply through a branch of the renal artery.
The afferent arteriole forms a fine capillary network in the form of glomerules with loftier hydrostatic pressure. The lumen between ii layers of Bowman's capsule is continuous with the lumen of the tubule. The Bowman's capsule and the glomerulus together form a globular body, the Malpighian body or the renal capsules.
The capillaries forming the glomerulus at the exit of Bowman's sheathing unite to form a narrow efferent arteriole which breaks up into a peritubular network of capillaries with low hydrostatic pressure.
The renal tubule is a long highly coiled tubular structure differentiated into proximal convoluted tubule (Pct) Henle's loop, distal convoluted tubule (DCT). The U-shaped loop-like structure, descending and ascending from the renal tubule is chosen Henle'south loop.
Collecting tubules of several nephrons open up into a wider duct called the collecting duct. A number of collecting ducts unite with each other in the medulla to course the ducts of Bellini, which drains down the urine into the ureter from each kidney to be stored in the urinary bladder.
The efferent arteriole emerges out from the glomerules breaks up into a peritubular capillary network around the renal tubule in the cortex. These capillaries besides grade a thin-walled, straight capillary the vasa recta. The vasa recta assistance in retaining the reabsorbed ions and urea in medullary interstitial fluid to maintain high osmotic pressure in kidneys.
Glomerular filtrate undergoes tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion for the formation of urine. (See diagram reverse page)
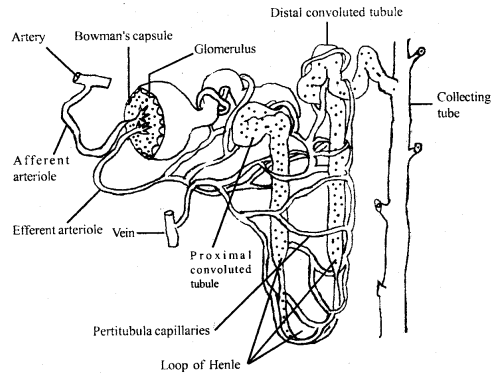
Uriniferous tubules Or nephron of the kidney
Question iv.
Depict the gross anatomical features of the homo kidney with a suitable diagram.
Respond:
Kidney: Kidney is chocolate brown, bean-shaped, large-sized about ten cm long and v – vii cm broad, three – 4cm thick flattened, metamorphic. The weight of each kidney is 150 to 170 gm. They are situated against the back wall of the abdominal cavity, just below the diaphragm, betwixt the 12th thoracic and 3rd lumbar vertebrae.
The outer margin is convex. The inner concave presents a longitudinal opening called the hilum. The renal artery and renal vein respectively enter and leave the kidney through its hilum.
The two kidneys are slightly asymmetrical in position because the right kidney is slightly at a lower level than the left. Kidneys are held in position past a mass of adipose tissue called Renal fat. These residue against the intestinal muscles. Each kidney is covered on the ventral side by the peritoneum and is thus retroperitoneal in nature.
Surrounding the kidneys and the renal fatty is a sheath of fibro elastic tissue known as renal fascia or capsule. They protect the kidney. The renal fatty forms a stupor-absorbing cushion. The renal fascia fixes the kidney to the abdominal wall.
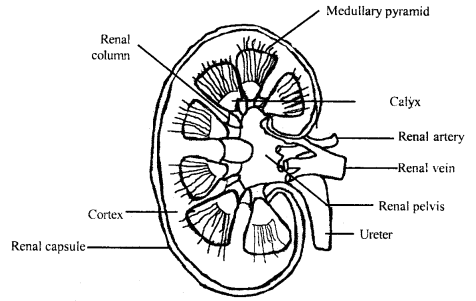
Longitudinal section (Diagrammatic of Kidney)
Question 5.
(a)What is the role of the liver in excretion in mammals?
Answer:
Role of liver in excretion: The liver changes ammonia into urea which is less toxic than ammonia. Urea is eliminated from the body past the kidneys through urine.
The liver is the principal organ of excretion of cholesterol, bile pigments (bilirubin and biliverdin) some vitamins, drugs, and inactivated products of steroid hormones. The liver excretes these substances in the bile which carries them to the small intestine. Ultimately, these substances go eliminated forth with feces.
(b) What are the diseases associated with the urinary arrangement?
Answer:
Diseases associated with the urinary system:
1. Polynephritis: It is a bacterial infection, which causes inflammation of renal pelvic nephrons and medullary tissues of the kidney. It affects the counter-current mechanism. Its primary symptoms are frequent and painful urination, fever, and pain in the lumbar region.
two. Uremia: Information technology causes the presence of a high concentration of urea, uric acrid, creatinine, etc, in the blood due to some bacterial infection or some obstruction in the passage of the urinary system. Urea poisons the cells. It is not passed in the urine and accumulates in the blood.
3. Renal stones: When uric acrid precipitates and accumulates in the nephrons of kidneys in the form of renal stones or when calcium phosphates and oxalates accrue in the nephrons of the kidneys in the course of renal stones. Information technology causes blockage or frequent painful urination forth with blood in the urine. Renal stone causes astringent colic hurting starting in the back and radiating down to the front of the thigh or vulva or testicle on that side.
four. Glomerulonephritis: It is characterized by the inflammation of Glomeruliduct, some injury to the kidney, abnormal allergic reaction, or past some streptococci leaner infection. Proteins and carmine blood corpuscles get filtered into the glomerular filtrate. It may pb to kidney failure in severe infection.
5. Oedema: It is characterized by the increased book of interstitial fluid mainly caused by retentivity of excess Na+ ions which in turn causes water retention. Blood pressure increases dining edema.
Question 6.
Write a short account on hemodialysis.
Answer:
In example of renal failure, an artificial kidney is used for removing excess urea from the blood of the patient by a process called hemodialysis. Claret is taken out from the avenue of the patient, cooled to 0°C, mixed with an anticoagulant such as heparin, and and so pumped into the appliance called artificial kidney. In this apparatus, blood flows through channels
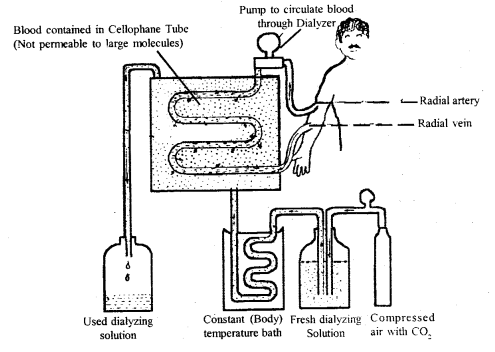
Working of artificial kidneys for hemodialysis
bounded past cellophane membrane. The membrane is impermeable to macromolecules but permeable to modest solutes. The membrane separates the blood flowing inside the channels from a dialyzing fluid flowing outside the membrane. The wastes like urea, uric acid, and creatinine diffuse from the claret to the dialyzing fluid across the cellophane membrane.
Thus the blood is considerably cleared of nitrogenous waste matter products without losing plasma proteins. Such a processor separation of macromolecules from small solute particles with the assistance of a permeable membrane is chosen dialysis. The blood coming out of the artificial kidney is warmed to trunk temperature, mixed with an Antiheparin to restore its normal coagulability, and returned to a vein of the patient.
Haemodialysis saves and prolongs the life of many uremic patients.
Source: https://www.tetsuccesskey.com/2021/04/excretory-products-and-their-elimination-class-11-important-extra-questions-biology-chapter-19.html
0 Response to "​what Is Abnormal Backflow of Urine From the Bladder to the Ureter Called?"
Post a Comment